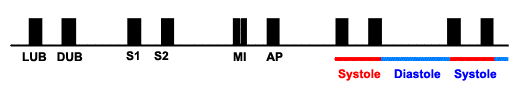
NORMAL HEART SOUNDS - S1 S2 (LUB-DUB)
S1 COMPONENT
- S1 produced when ventricles contract causing closure of AV valves - mitral and tricuspid valves
- S1 is loudest at apex of heart
- The left ventricle is capable of generating higher pressures more quickly
- Mitral valve (left ventricle) closes slightly before the tricuspid (right ventricle) due pressure difference
- The two sounds slightly overlap and create
one sound - S1
- In reality, the first half of S1 is the mitral component
- Second half of S1 is the tricuspid contribution
- With practice (much practice!) individual components of S1 and S2 can be appreciated
- S1-S2 are easier to distinguish at slower heart rates (e.g. 56 bpm);
- Discerning S1 and S2 is difficult at higher rates
- S1 is always after the longer pause
- As heart rate
increases, systole time is constant; diastole
time shortens
- Distinction (S1 and S2) is challenging at faster heart rates
- Keeping finger on pulse is useful aid to distinguish S1 from S2
- Pulse felt between S1 and S2 at the neck
- S2 produced with closure of semilunar valves - aortic and pulmonic valve
- S2 is loudest at base of heart
- Aortic
valve closes slightly ahead
of pulmonic creating
two component
- A2 and P2 indicate aortic and pulmonic component respectively
- A2 normally precedes P2 (aortic valve closes before pulmonic valve)
- Inspiration lowers intrathoracic pressure thus draws more blood from both venae cavae
- Increased blood volume (from inspiration) requires more time to eject all blood into PA
- Pulmonic valve thus stays open longer thus P2 occurs later with inspiration vs expiration
- Difference is called physiologic split (covered later under Spit

|

|